In programming, we use an algorithm to determine a clearly defined set of commands used to accomplish a specific task. Two things are important to make your life easier; Pseudocode and flowchart.
Flowchart
A flowchart is a diagram that shows a sequence of steps using standardized shapes such as rectangles to represent actions, rhombuses to represent decisions, and arrows to show algorithm flow. It can also be defined as a step-by-step approach to solving a task. It shows the steps as boxes of different types, and their order by connecting the boxes with arrows.
Pseudocode
A pseudocode is a written set of instructions that follow a certain structure. It looks more like code, but cannot be executed by a computer. Once you have written the pseudocode, the algorithm can then be coded in any programming language you want, using the same pseudocode.
Why use pseudocode?
- Since computer scientists may work alongside people from other fields who are unfamiliar with programming, pseudocode can help explain the mechanics of your algorithm.
- Pseudocode can be useful as a starting point for your documentation. We all know how annoying poorly written documentation is. Pseudocode can be a good starting point for what the documentation should include.
- It helps to visualize what you are about to code and can help with bug detection. Since the pseudocode is written in a language you are familiar with (usually English), it is easier to catch and fix any bugs in your code, which can save you a lot of time and effort, and save you a lot of headaches.
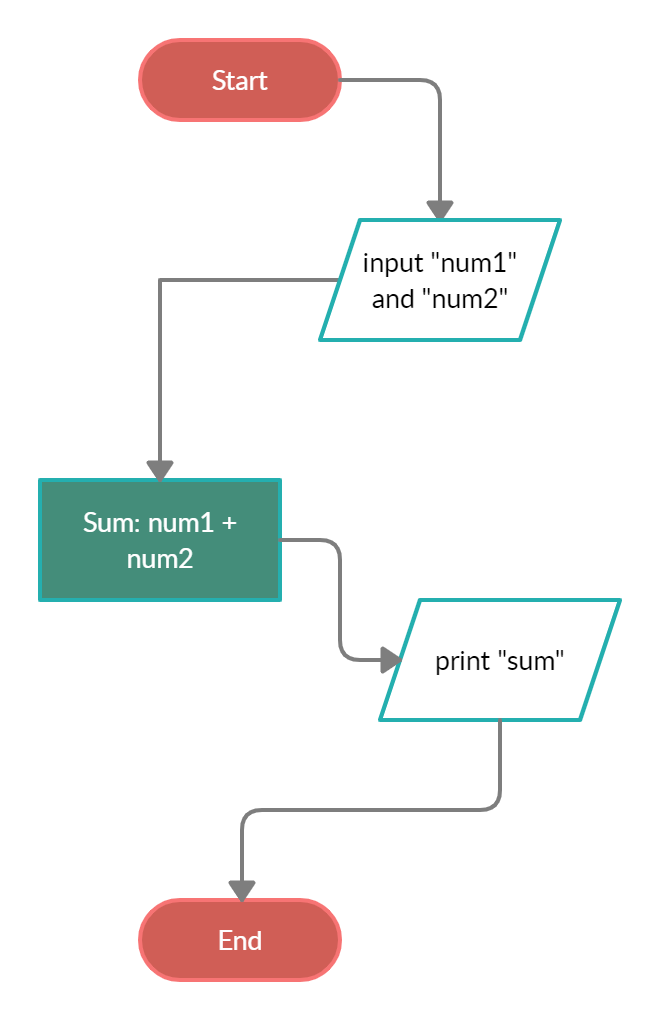
Then, the pseudocode of the flowchart above will be:
- Start the program
- Input the first number and save it in the variable "num1"
- Input the second number and save it in the variable "num2"
- Sum both numbers and save the result in the variable "sum"
- Print the variable "sum"
- End the program
You can create your own flowchart with your tablet, or using one of this three software (recommended by my Python class teacher last fall):
Happy coding! 😄